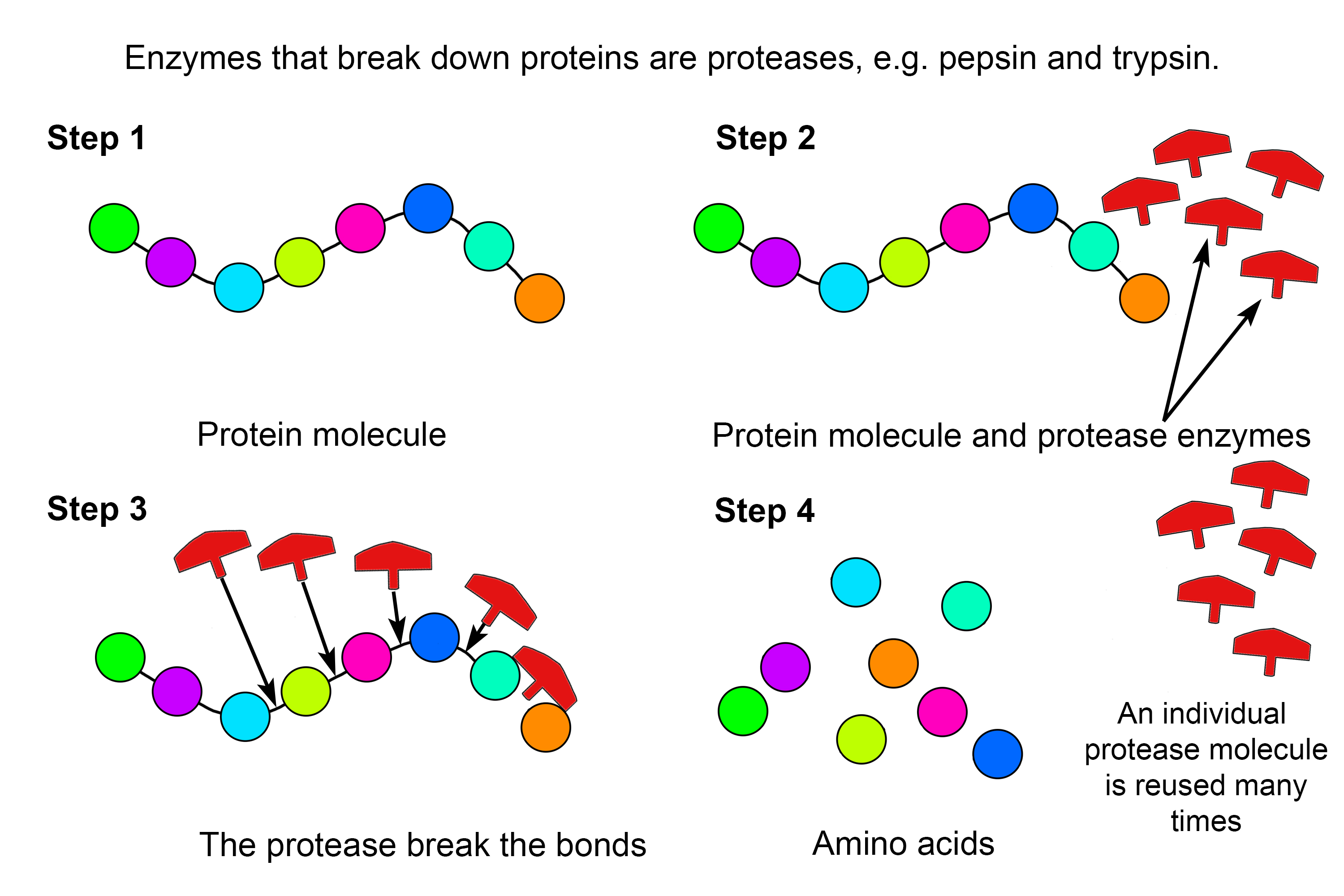
Enzymes are essential components of life; they are responsible for catalyzing hundreds of biochemical reactions in our bodies. One important enzyme is protease, which is responsible for breaking down proteins. In this article, we will explore what protease is, how it works, and why it is important for proper digestion. We will also discuss the different types of proteases and why they are important for our health.
Proteases are enzymes that break down proteins. Proteases are hydrolytic enzymes, meaning they use water to break the peptide bonds that link amino acids together in a protein. Proteases are found in organisms from all domains of life, and are essential for many biological processes, such as digestion, immune response, and cell cycle regulation. Proteases also have industrial and pharmaceutical applications.
How To Make Protein Shakes:
- Gather your ingredients – protein powder, water, milk, ice cubes, and any other desired ingredients.
- Measure out the desired amount of protein powder.
- Add the protein powder to a blender.
- Slowly add the desired amount of liquid to the blender.
- Add any additional ingredients you would like to the blender.
- Mix the ingredients together until the shake is the desired texture.
- Enjoy your delicious protein shake!
Protein vs Carbohydrates:
| Protein | Carbohydrates |
|---|---|
| Amino Acids | Monosaccharides |
| Used for growth, repair and maintenance of the body. | Used mostly for energy. |
| Aids in optimal functioning of organs and tissues. | Aids in digestion of nutrients. |
| Not stored as energy. | Stored as glycogen. |
What are Proteins?
Proteins are complex molecules made up of amino acid chains. They are a vital component of all living organisms and are essential for many biochemical processes, including DNA synthesis, muscle contraction, and cellular metabolism. Proteins are vital components of all cells, tissues, and organs and are used in the production of hormones, enzymes, and other proteins. Proteins are also responsible for the structure and function of many of the body’s organs and tissues, including muscles, skin, and bones.
What is an Enzyme?
An enzyme is a protein or a protein-like molecule, which acts as a catalyst in biochemical reactions. Enzymes are responsible for breaking down molecules, speeding up chemical reactions, and helping to make complex molecules. Enzymes are found in most living organisms and are essential for the functioning of cells and for the production of energy. Enzymes are also involved in the digestion of food, the breakdown of toxins, and the production of hormones.
Which Enzyme Breaks Down Protein?
The enzyme that breaks down proteins is called protease. Proteases are enzymes that break down proteins into smaller peptide fragments, which can then be further broken down by other enzymes. Proteases are found in all living organisms, including bacteria, fungi, plants, and animals. Proteases are responsible for the digestion of proteins, and they play an important role in the metabolism of amino acids and proteins.
Types of Proteases
There are several different types of proteases, including serine proteases, cysteine proteases, and aspartic acid proteases. Serine proteases are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in proteins. Cysteine proteases catalyze the hydrolysis of disulfide bonds in proteins. Aspartic acid proteases are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of aspartic acid residues in proteins.
How Proteases Work
Proteases work by breaking down proteins into smaller peptides or amino acids. The enzyme binds to the protein, and then cleaves the peptide bond between two amino acids. This releases the smaller peptides. These smaller peptides are then further broken down by other enzymes into their constituent amino acids.
The Role of Proteases in the Body
Proteases play an important role in the metabolism of proteins in the body. Proteases are involved in the digestion of food, the breakdown of toxins, and the production of hormones. Proteases are also necessary for the absorption of nutrients in the intestines and for the production of energy in the body.
Proteases and Disease
In some cases, the activity of protease enzymes can be disrupted, leading to disease. For example, some proteases are involved in the breakdown of amyloid-beta proteins, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease. In this case, a decrease in the activity of proteases can lead to an accumulation of these proteins and the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
Regulation of Proteases
The activity of proteases is regulated by several different mechanisms. For example, some proteases are activated by specific signals, such as hormones, while others are inhibited by certain molecules. Proteases can also be regulated by other proteins, such as inhibitors, which can block their activity.
Protease Inhibitors
Protease inhibitors are molecules that can block the activity of proteases. They can be used to treat a variety of diseases, including HIV/AIDS, cancer, and cystic fibrosis. Protease inhibitors are also used to inhibit the activity of enzymes involved in the formation of amyloid-beta proteins, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Uses of Proteases in Industry
Proteases are used in a wide variety of industrial applications, including food processing, detergent manufacturing, and biofuel production. Proteases are also used to produce enzymes for medical and pharmaceutical applications, such as the production of antibiotics, vaccines, and therapeutic proteins.
Safety Precautions When Working with Proteases
When working with proteases, it is important to take safety precautions to avoid potential hazards. Proteases can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system, and should be handled with care. Proper protective clothing and equipment, such as gloves and goggles, should be worn when handling proteases.
Conclusion
Proteases are enzymes that play an important role in the metabolism of proteins in the body. They can be found in all living organisms and are involved in the digestion of food, the breakdown of toxins, and the production of hormones. Proteases are also used in a variety of industrial applications and can be regulated by various mechanisms, including inhibitors. When working with proteases, it is important to take safety precautions, such as wearing protective clothing and equipment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Enzyme?
An enzyme is a type of protein produced by living organisms. They act as catalysts in metabolic processes and are essential for the functioning of the body. Enzymes work by binding with specific molecules and speeding up the rate at which chemical reactions occur. In this way, they facilitate the breakdown of complex molecules, such as proteins and carbohydrates, into simpler molecules that the body can use.
Which Enzyme Breaks Down Protein?
The enzyme that breaks down proteins is called protease. Proteases are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds, which are the bonds that link amino acids together to form proteins. Proteases are found in all living organisms and are involved in many biological processes, such as digestion and protein metabolism.
What is the Role of Protease in Digestion?
The role of protease in digestion is to break down proteins into smaller molecules, such as amino acids, which can then be absorbed by the body. Proteases are secreted by the pancreas and other organs in the digestive tract and act on proteins in the food we eat, breaking them down into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body. This process is essential for the body to be able to utilize the proteins in our diet.
How Does Protease Work?
Proteases work by cleaving peptide bonds in proteins, which are the bonds that link amino acids together. The protease enzyme binds with the protein molecule and catalyzes the reaction that breaks the peptide bonds, which causes the protein to be broken down into smaller molecules. This process is essential for the body to be able to absorb and utilize the proteins in our diet.
What Happens if Protease Levels are Too High?
If protease levels are too high, it can lead to problems such as digestive issues and malabsorption of nutrients. High levels of protease can also lead to the breakdown of other proteins in the body, which can cause further health issues. It is important to ensure that protease levels are kept within the normal range to ensure good health.
Protein Metabolism Overview, Animation
In conclusion, the enzyme that breaks down protein is called protease. Protease is a type of enzyme that is essential for the digestion of proteins in our bodies. It is found in many different forms and is responsible for the breakdown of proteins into smaller components. This is a vital part of the digestion process and helps our bodies to absorb important nutrients and stay healthy.